Optipedia • SPIE Press books opened for your reference.
Explanation of defocus from Field Guide to Optical Lithography
Excerpt from Field Guide to Optical Lithography
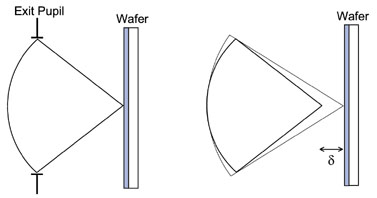
The impact of focus errors on the resulting aerial image can be described as equivalent to an aberration of a sort. By viewing the actual wavefront as having an error in curvature relative to the desired wavefront (i.e., the one that focuses on the wafer), we can quantify the effect of defocus. The distance between wavefronts is called the optical path difference (OPD). Describing the position within the exit pupil by an angle θ, the optical path difference is given by
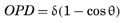
A Taylor expansion in terms of sinθ gives
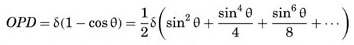
For small angles (that is, small numerical apertures), the impact of defocus is approximately
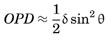
Defocus causes a phase error that is zero at the center of the pupil and approximately quadratic across the pupil.
C. A. Mack, Field Guide to Optical Lithography, SPIE Press, Bellingham, WA (2006).
View SPIE terms of use.

